Lake Mweru is located on the longest arm of the Congo River, approximately 150 km west of Lake Tanganyika. Extensive adjoin it to the east and south. The lake shoreline contains many fishing villages. The lake does not exhibit major water level changes, in spite of pronounced wet and dry seasons, being attributed to the Bangweulu swamps that tend to absorb the annual floods and release them slowly, as well as the outflowing Luvua River, which tends to flow faster during flood periods. Despite being considered a beautiful lake, it has not been developed extensively for tourism, attributed mainly to a lack of wildlife conservation and wars in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The lake supports fisheries, mining and some tourism industries, although the magnitude of their environmental impacts is not clear. Any potential management interventions should be considered together with Lakes Rweru/Moero and Cohoha.
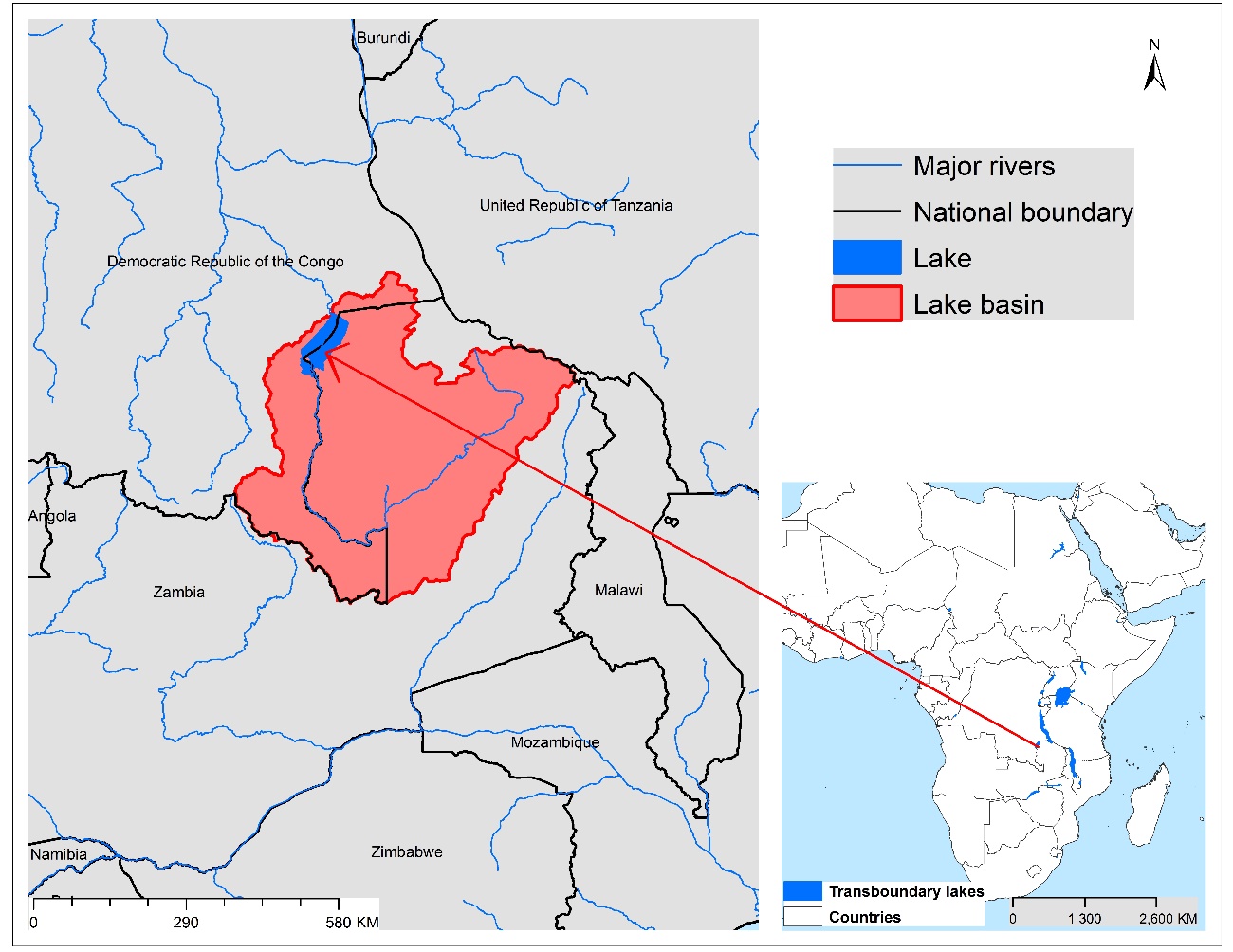
| TWAP Regional Designation | Eastern & Southern Africa; Western & Middle Africa | Lake Basin Population (2010) | 4,269,364 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| River Basin | Congo | Lake Basin Population Density (2010; # km-2) |
17.2 | |
| Riparian Countries | Democratic Republic of Congo, Zambia | Average Basin Precipitation (mm yr-1) |
1,200 | |
| Basin Area (km2) | 29,429 | Shoreline Length (km) | 681.3 | |
| Lake Area (km2) | 179,444 | Human Development Index (HDI) | 0.38 | |
| Lake Area:Lake Basin Ratio | 0.023 | International Treaties/Agreements Identifying Lake | No |
Lake Mweru Basin Characteristics
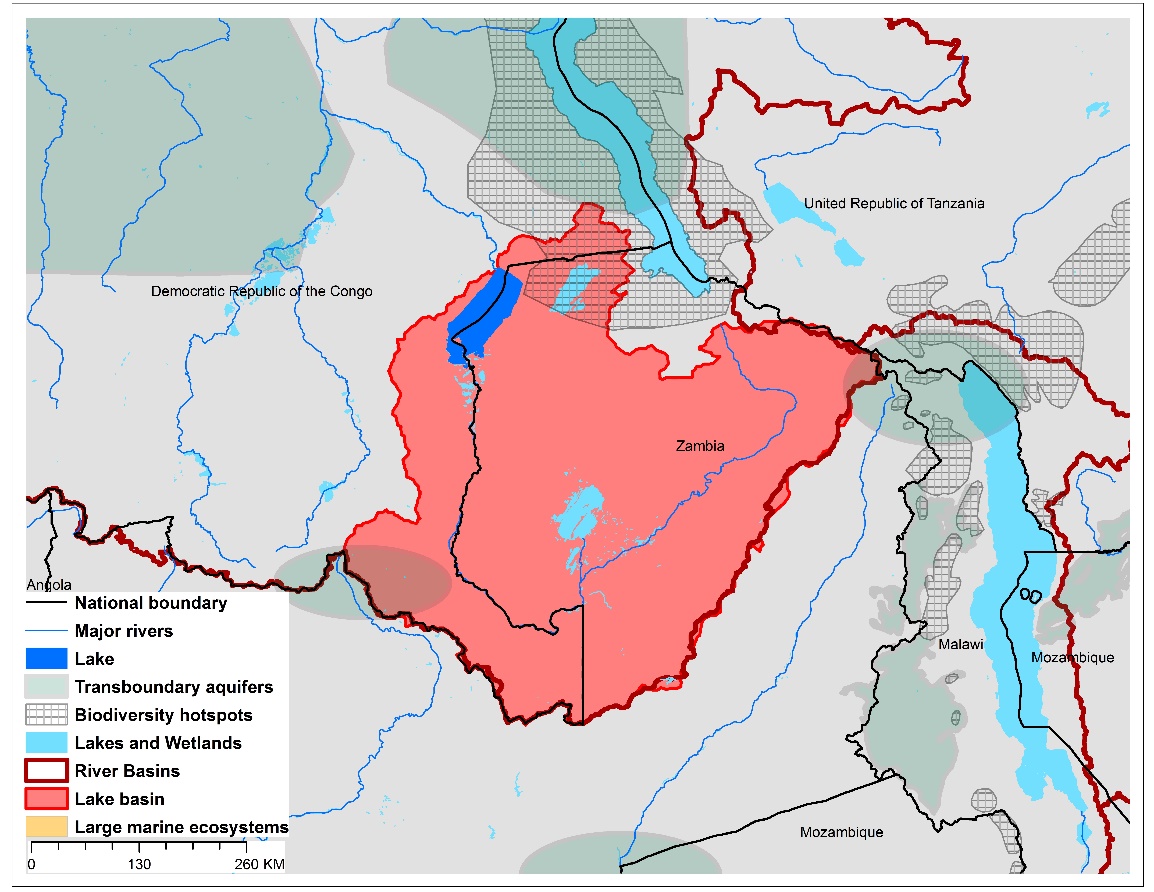
(a)Lake Mweru basin and associated transboundary water systems
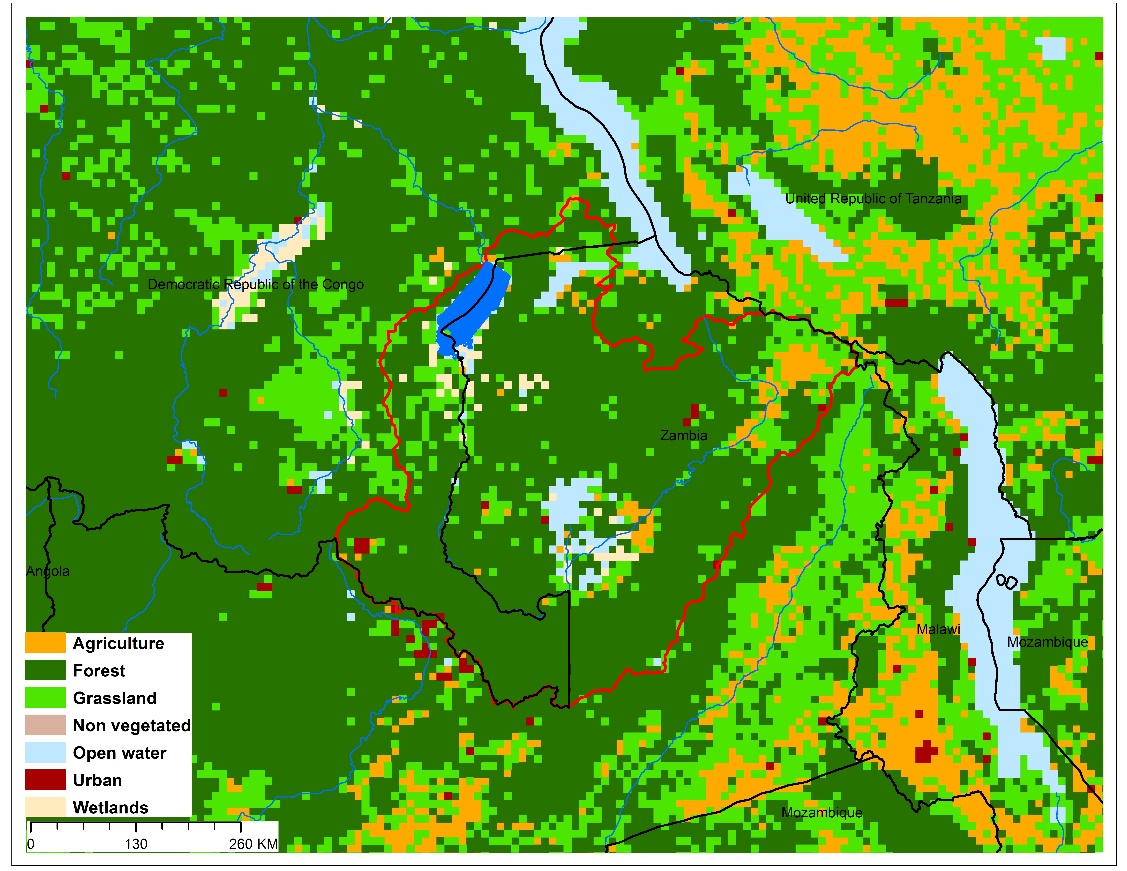
(b)Lake Mweru basin land use
A serious lack of global-scale uniform data on the TWAP transboundary in-lake conditions required their potential threat risks be estimated on the basis of the characteristics of their drainage basins, rather than in-lake conditions. Using basin characteristics to rank transboundary lake threats precludes consideration of the unique features that can buffer their in-lake responses to basin-derived disturbances, including an integrating nature for all inputs, long water retention times, and complex, non-linear response dynamics.
The lake threat ranks were calculated with a spreadsheet-based interactive scenario analysis program, incorporating data and information about the nature and magnitude of their basin-derived stresses, and their possible impacts on the sustainability of their ecosystem services. These descriptive data for Lake Mweru and the other transboundary lakes included lake and basin areas, population numbers and densities, areal extent of basin stressors on the lake, data grid size, and other components considered important from the perspective of the user of the data results. The scenario analysis program also provides a means to define the appropriate context and preconditions for interpreting the ranking results.
The Lake Mweru threat ranks are expressed in terms of the Adjusted Human Water Security (Adj-HWS) threats, Reverse Biodiversity (RvBD) threats, and the Human Development Index (HDI) score, as well as combinations of these indices. However, it is emphasized that, being based on specific characteristics and assumptions regarding Lake Mweru and its basin characteristics, the calculated threat scores represent only one possible set of lake threat rankings. Defining the appropriate context and preconditions for interpreting the lake rankings remains an important responsibility of those using the threat ranking results, including lake managers and decision-makers.
(Estimated risks: red – highest; orange – moderately high; yellow – medium;
green – moderately low; blue – low)
| Adjusted Human Water Security (Adj-HWS) ThreatScore |
Relative Adj-HWS Threat Rank | Reverse Biodiversity (RvBD) Threat Score | Relative RvBD Threat Rank | Human Development Index (HDI) Score | Relative HDI Rank | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.81 | 33 | 0.72 | 4 | 0.38 | 6 |
It is emphasized that the Lake Mweru rankings above are discussed here within the context of the management and decision-making process, rather than as strict numerical ranks. Based on its geographic, population and socioeconomic assumptions used in the scenario analysis program, the calculated Adj-HWS score for Lake Mweru indicates a medium threat rank compared to other priority transboundary lakes.
The Reverse Biodiversity (RvBD) for Lake Mweru, which is meant to describe its biodiversity sensitivity to basin-derived degradation, reveals a different picture, placing the lake in a high threat rank, compared to the other transboundary lakes. Management interventions directed to improving the biodiversity status must be viewed with caution, however, since we lack sufficient knowledge and experience to accurately predict the ultimate impacts of biodiversity manipulations and preservation efforts. Further, the RvBD scores indicate the relative sensitivity of a lake basin to human activities, and high threat scores per se do not necessarily justify management interventions. Such interventions may actually increase biodiversity degradation, noting that many developed countries have already fundamentally degraded their biodiversity because of economic development activities. Thus, activities undertaken to address the Adj-HWS threats may actually degrade the biodiversity status and resources, even if the health and socioeconomic conditions of the lake basin stakeholders are improved as a result of better conditions, thereby increasing stakeholder resource consumption.
The relative Human Development Index (HDI) places the Lake Mweru basin in a high threat rank in regard to its health, educational and economic status.
(Scores for Adj-HWS, RvBD and HDI ranks are presented in Table 1; the ranks may differ in some cases because of rounding of figures; Estimated risks: red – highest; orange – moderately high; yellow – medium;
green – moderately low; blue – low)
| Adj-HWS Rank | HDI Rank | RvBD Rank | Sum Adj-HWS + RvBD | Relative Threat Rank |
Sum Adj-HWS + HDI | Relative Threat Rank | Sum Adj-HWS + RvBD + HDI | Overall Threat Rank | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 33 | 6 | 4 | 43 | 24 | 33 | 16 | 42 | 12 |
When multiple ranking criteria are considered together in the threat rank calculations, the Adj-HWS and HDI scores considered together place Lake Mweru in the upper third of the threat ranks. The relative threat increases somewhat when the Adj-HWS and RvBD threats are considered together. Considering all three ranking criteria together, Lake Mweru exhibits an overall moderately high threat ranking.
Further, a series of parametric sensitivity analyses of the ranking results also was performed to determine the effects of changing the importance of specific criteria on the relative transboundary lake rankings. This analysis involved increasing or decreasing the weights applied to the threat ranks derived from multiple ranking criteria to reassess the relative impacts of the weight combinations on the threat ranks. For example, in determining the sensitivity of the Adjusted Human Water Security (Adj-HWS) and Biodiversity (BD) ranking criteria, the threat rank associated with the first was assumed to be of complete (100%) importance (i.e., rank weight of 1.0), while the other was assumed to be of no (0%) importance (i.e., rank weight of 0.0). The relative importance of the two ranking criteria was then successively changed, with weight combinations of 0.9 and 0.1, 0.8 and 0.2, etc., until the first ranking criteria (Adj-HWS) was assumed to be of no importance (rank weight of 0.0) and the second (BD) was of complete importance (rank weight of 1.0). In the case of Lake Mweru, the 0.5 and 0.5 weight combinations for three cases of parametric analysis for Lake Mweru resulted in respective threat rankings of 22nd, 13th and 22nd, respectively, among the total of 23 African transboundary lakes in the TWAP study (see Technical Report, Section 4.3.3, pp44-49).
In essence, therefore, identifying potential management intervention needs for Lake Mweru must be considered on the basis of both educated judgement and accurate representations of its situation. A fundamental question to be addressed, therefore, is how can one decide that a given management intervention will produce the greatest benefit(s) for the greatest number of people in the Lake Mweru basin? Accurate answers to such questions for Lake Mweru, and other transboundary lakes, will require a case-by-case assessment approach that considers the specific lake situation and context, the anticipated improvements from specific management interventions, and its interactions with water systems to which the lake is linked. To this end, it is noted that the African transboundary lakes as a group merit special attention in regard to management interventions, with some lakes requiring more immediate attention than others.